Connective tissue support, protect and bind
together other tissue. Connective tissue is the diversity of cells which
containing large quantity of extracellular matrix. Connective tissue origin from mesenchyme. Connective tissue is most abundant and widespread tissue in our human body.
Composition of connective tissue
Connective tissue consist of two basic elements -
- Cells
- Extracellular matrix
Cells in connective tissue
Each of major type of connective tissue contains an immature category of cells with a name ending in -'blast'.
Immature cells
- In loose connective tissue, called "fibroblasts"
- In dense connective tissue
- Cartilage, called Chondroblasts
- Bone, called Osteoblasts
Blast cells retain the capacity for cell division and secrete the extracellular matrix.
Mature cells with names ending in -'cyte'.
- Cartilage called chondrocytes
- Bone called osteocytes
Type of cells in connective tissue
Many cells help in making connective tissue. Following cells are involve in composition of connective tissue -
- Fibroblasts
- Macrophages - engulfing bacteria and cellular debris by phagocytosis
- Plasma cells
- Mast cells
- Adipocytes cells or fat cells - store fat
- White blood cells (WBC)
Extra cellular matrix (ECM)
Extra cellular matrix located between cells space. Extra cellular matrix consist of two components.
- Protein fibers
- Ground matrix
Protein fibers
Three types of fibers are help to making connective tissue.
- Collagen fibers
- Elastic fibers
- Reticular fibers
Ground substance
- Material between cells and fibers are called ground substance.
- Ground substance may be fluid, gelatinous or calcified.
- Ground substance support cells.
- Ground substance help to binds them together.
- Ground substance provide medium for exchange of substances between blood and cells.
- Ground substance store water.
- Water and organic molecules
- Complex combination of polysaccharides and proteins
Complex combination of polysaccharides includes -
- Hyaluronic acid
- Chondroitin sulfate
- Dermatan sulfate
- keratan sulfate
- Water and organic molecules
- Complex combination of polysaccharides and proteins
Complex combination of polysaccharides includes -
- Hyaluronic acid
- Chondroitin sulfate
- Dermatan sulfate
- keratan sulfate
Classification of connective tissue
- Loose connective tissue
- Areolar connective tissue
- Adipose connective tissue
- Reticular connective tissue
- Dense connective tissue
- Dense regular connective tissue
- White fibrous connective tissue
- Yellow fibrous connective tissue
- Dense irregular connective tissue
- Elastic connective tissue
- Skeletal connective tissue
- Bone
- Compact bone
- Spongy bone
- Cartilage
- Hyaline cartilage
- Fibrocartilage
- Elastic cartilage
- Vascular connective tissue
- Blood tissue
- Lymph
- Muscular tissue
- Cardiac muscle tissue
- Skeletal muscle tissue or striated muscle or striped muscle or voluntary muscle
- Smooth muscle tissue or non-striated muscle or visceral muscle or involuntary muscle.
Areolar connective tissue
Areolar connective tissue consists of fibers (collagen, elastic and reticular) and several types of cells (Fibroblasts, macrophages, adipocytes, mast cell, plasma cell and other kinds of blood cells). Areolar connective tissues are one of the most distributed connective tissue.
Composition of areolar connective tissue
- Fibers - Collagen, elastic and reticular
- Cells - Fibroblasts, macrophages, adipocytes, mast cell, plasma cell and other kinds of blood cells
Location of areolar connective tissue
- Subcutaneous deep to skin
- Around blood vessels
- Nerve
Function of areolar connective tissue
- Areolar connective tissue provide support, elasticity and strength.
Adipose connective tissue
Adipose tissue composed with fibroblast cells (also known as adipocytes cells) that cells are specialized for storage for fats (triglycerides).
Composition of adipose tissue
- Cells: adipocytes or fibroblast
Location of adipose tissue
- Around the heart
- Kidneys
- Behind eyeball
Function of adipose tissue
- Protects and supports body organs
- Reduces heat loss through skin
- In new born, Generate heat to maintain normal body temperature.
 |
| Adipose connective tissue |
Reticular connective tissue
Composition of reticular connective tissue
- Fiber: reticular fibers
- Cells: reticular cells
Location of reticular connective tissue
- Spleen
- Lymph nodes
- Red bone marrow
Function of reticular connective tissue
- Help to binds smooth muscle tissue (SMT) cells.
- Help to form stroma (shape) organ.
- Help to remove aged blood cells in spleen
Dense connective tissue
The fibers arranged between the cells are thick and closely packed. Dense connective tissues are three types -
Dense regular connective tissue
Dense connective tissue are two types
- White fibrous connective tissue : For example - Tendons
- Yellow fibrous connective tissue : For example - Ligaments
Composition of dense regular connective tissue
- Fibers: mainly collagen fibers are regularly arranged in bundles. Fibroblast present in rows between bundles.
- Matrix: white and shiny
Location of of dense regular connective tissue
- Tendons (binds muscle to bone)
- Ligament (binds bone to bone)
Function of of dense regular connective tissue
- Provide strong attachment between many structure such as ligaments and tendons
Dense irregular connective tissue
Composition of dense irregular connective tissue
- Fibers: Collagen fibers are irregularly arranged in bundles
- Few fibroblast.
Location of dense irregular connective tissue
- Fibrous pericardium of heart
- Heart valve
- Joint capsule
Function of dense irregular connective tissue
- Help to pulling strength in many directions.
 |
| Dense irregular connective tissue |
Elastic connective tissue
Composition of elastic connective tissue
- Elastic fibers are arranged with fibroblast
Location of elastic connective tissue
- Wall of elastic arteries,
- Lung tissue
- Bronchial tube
Function of elastic connective tissue
- Allow stretching of various organs for example; lung- inhale or exhale.
- After stretching recoil to original shape of organ.
 |
| Elastic connective tissue |
Hyaline cartilage
Composition of hyaline cartilage
- Resilient gel
- Fine collagen fibers
Location of hyaline cartilage
- Nose
- Trachea
- At the end of bones and fetal skeleton etc
Function of hyaline cartilage
- Provide surface for support and flexibility.
- It help for movement at joint, hyaline cartilage present at both end of bone, it reduce the fraction.
 |
| Hyaline cartilage |
Fibrocartilage
Composition of fibrocartilage
- Thick collagen fibers
- Perichondrium absent
Location of fibrocartilage
- Cartilage pad of knee
- Intervertebral disc
Function of fibrocartilage
Elastic cartilage
Composition of elastic cartilage
- Elastic fibers
- Perichondrium
Location of elastic cartilage
- External ear
- Epiglottis
Function of elastic cartilage
- Help to maintain shape of certain structure of organs of body.
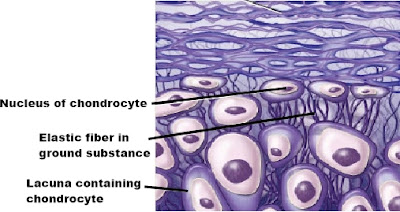 |
| Elastic cartilage |
Muscular tissue
Muscular tissues consist of muscle fibers that can use ATP to generate force. Muscular tissues generate heat, produce body movement and maintain body posture.
Muscular tissues are classified into 3 types -
Muscular tissues are classified into 3 types -
Skeletal muscle tissue
- Skeletal muscle tissues consist of long, cylindrical and striated fibers.
- Skeletal muscles are voluntary nature because it contract and relax by conscious control.
Location of skeletal tissue
- Skeletal muscle tissues are attached to bone by tendons.
Functions of skeletal tissue
- Heat production
- Protection
- Body posture
- Body movement
Cardiac muscle tissue
- Cardiac muscles are consists with branched striated fibers and a centrally located nucleus.
- Cardiac muscle tissues are involuntary nature because it contract and relax by unconscious control.
Location of cardiac muscle tissue
- Heart wall
Function of cardiac muscle tissue
Smooth muscle tissue
- Smooth muscle tissues are consist nonstriated fibers.
- These fibers are consists with small spindle shaped cells and containing single centrally located nucleus.
- Smooth muscle tissues are usually involuntary.
Location of smooth muscle tissue
- Walls of hollow internal structures such as gall bladder, intestine, stomach, uterus, airway to lungs and blood vessels.
Function of smooth muscle tissue
- Contraction and movement of intestine, stomach, uterus, airway to lungs and blood vessels.
 |
| Smooth muscle tissue |






0 comments:
Post a Comment